That, if applied widely, could change the pace and structure of an operation.
“By achieving excellent image quality in fresh tissues, we're able to make a diagnosis during surgery,” says first author Daniel A. Orringer, M.D., assistant professor of neurosurgery at the University of Michigan Medical School. “This eliminates the lengthy process of sending tissues out of the OR for processing and interpretation.”
Today’s workflow for determining a diagnosis during an operation requires the surgeon wait for 30 to 40 minutes while tissue is sent to a dedicated pathology lab for processing, sectioning, staining, mounting and interpretation. The entire team in the operating room may be idle while waiting for pathology results, Orringer says.
A more efficient surgical procedure would save money by requiring less time in the operating room.
“Our technique may disrupt the intraoperative diagnosis process in a great way, reducing it from a 30-minute process to about 3 minutes,” Orringer says. “Initially, we developed this technology as a means of helping surgeons detect microscopic tumor, but we found the technology was capable of much more than guiding surgery.”
Near-perfect agreement
Stimulated Raman scattering microscopy, the technology behind SRH, was developed in 2008 (link is external), but the hazardous lasers it involved made it unsuitable for use in an operating room. A clinical version has now been developed and tested in the operating room for more than a year at U-M, with the fiber-laser-based microscope mounted right onto a clinical cart that plugs into the wall.
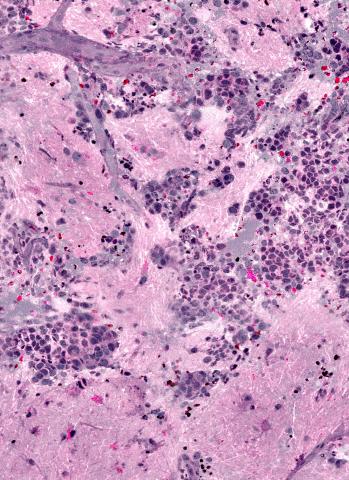
SRH uses virtual coloring to highlight the cellular and architectural features of brain tumors, with a result resembling traditional staining. The pathologist is then able to differentiate the tumor tissue from normal brain as usual.
“It’s very similar to what we currently do in our intraoperative diagnosis, with the exception that the tissue is fresh, has not been processed or stained,” says senior author Sandra Camelo-Piragua, M.D., assistant professor of pathology at the U-M Medical School.
In the Nature Biomedical Engineering study, neuropathologists were given 30 specimen samples, processed via SRH or traditional methods. They were told the same information about each patient’s medical history and the location of the tumor and asked to make a diagnosis.
Those pathologists, the U-M researchers found, were equally likely to make a correct diagnosis whether they used SRH or conventional slides.
“SRH imaging will ensure that appropriate and good quality tissue is collected to reach our ultimate goal: accurate diagnosis,” Camelo-Piragua says.
Artificial intelligence
As Orringer and his team continue to improve this imaging technology, they’re also teaching a computer how to use SRH images to make diagnoses.
They built and validated a machine learning process that was able to predict brain tumor subtype with 90 percent accuracy in a subset of 30 patient samples.
“The more we feed the computer, the more accurate its diagnoses will become,” Orringer says.
Connecting hospitals
Using SRH might also improve the workflow for facilities without access to expert neuropathologists. Orringer notes that smaller hospitals may be able to partner with larger systems that do have access, since there are fewer than 800 board-certified neuropathologists compared to the approximately 1,400 U.S. institutions performing brain surgery.
“Bringing the SRH to smaller hospitals would extend their capabilities because the images can be interpreted remotely,” he says. Sample preparation is minimal and the SRH could quickly deliver virtual histologic sections to aid diagnosis remotely.
The next step is a large-scale clinical trial, with an eventual goal of showing equivalence between SRH technique for making diagnoses, Orringer says. The prototype system is currently intended for research use only.
Additional authors from Michigan Medicine include Balaji Pandian, Yashar S. Niknafs, Todd C. Hollon, Julianne Boyle, Spencer Lewis, Mia Garrard, Shawn L. Hervey-Jumper, Hugh J. L. Garton, Cormac O. Maher, Jason A. Heth, Oren Sagher, D. Andrew Wilkinson, Sriram Venneti, Kathryn A. McFadden, Amanda Fisher-Hubbard, Andrew P. Lieberman and Timothy D. Johnson. Matija Snuderl is from New York University. Shakti H. Ramkissoon is from Harvard Medical School and the Dana Farber Cancer Institute. X. Sunney Xie is from Harvard University. Jay K. Trautman and Christian W. Freudiger are from Invenio Imaging.
This work was funded by the National Institutes of Health, Michigan Translational Research and Commercialization for Life Sciences Program (U-M MTRAC) and the Michigan Institute for Clinical and Health Research.